Description
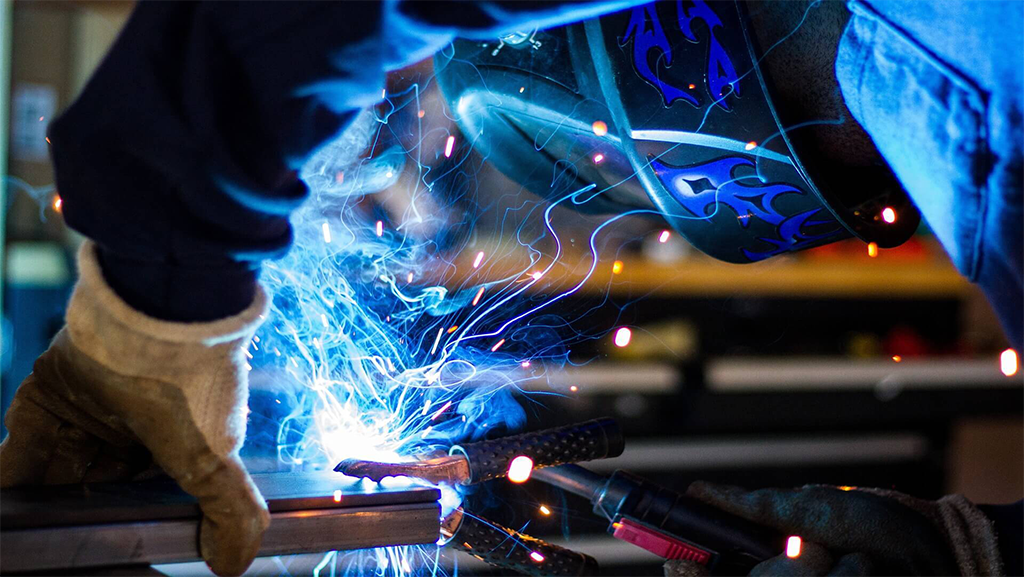
Welding process with TIG electrode
In the process of electric arc welding on non-consumable tungsten electrode with GTAW gas protection or (Gas Tungsten Arc Welding) which are called tungsten electrode welding, tungsten inert gas welding (TIG), tungsten-gas welding, Tig is also known as argon welding in Iran. An electric arc is created between the non-consumable electrode and the base metal, and the resulting temperature will cause the parts to melt and join.
The electrode used in this process is often made of tungsten alloy and the molten pool is protected by a neutral gas such as argon or helium. In this process, it is possible to use a consumable with a material similar to the base metal, which leads to an increase in the deposition rate and control of the chemical composition of the weld metal.
Chemical composition of tungsten electrodes
Tungsten electrodes used in the TIG welding process are in the group of non-melting electrodes and according to AWS A5.12 standard, their chemical composition is as follows:
Pure tungsten electrode
Tungsten-thorium electrode (containing 1 to 2% thorium oxide)
Tungsten-zirconium electrode (containing 0.15 to 0.4% zirconium oxide)
Tungsten-Lanthanum Electrode (Containing 1% Lantium Oxide)
Tungsten-cerium electrode (containing 2% cerium oxide)
Advantages of TIG tungsten electrode welding process
Excellent appearance of welding metal
No need for cleaning after welding
Excellent possibility to control welding
Suitable for root pass
Remarkable quality
Possibility of welding with or without the use of consumables







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.